Introduction
Although there are advancements in technology of transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) delivery systems, ICs occasionally encounter difficulty in delivering transcatheter heart valve (THV) delivery systems across the aortic valve in challenging cases. In this Tip-of-the-Month, a few strategies to overcome this issue are addressed. Most challenges are with the transfemoral approach.
Two Main Challenge Areas
- Difficulty in crossing the aortic arch:
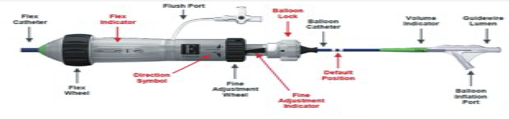
- The SAPIEN 3 THV(Edwards Lifesciences, Irvine, CA) has the Edwards Commander delivery system with a flex wheel to help with crossing the tortuous aortic arch (see Figure 1).
- For the Medtronic Evolut R THV (Dublin, Ireland) delivery system, the orientation of spines can be changed with the EnVeo PRO delivery system to overcome tortuosity of the aortic arch, although this may limit the ability to align the flush port at the 3 o’clock position for correct commissural alignment for coronary access post-TAVR1 (see Figure 2). Lining up the hat maker on the outer curve of the aorta puts the delivery system in the most favorable orientation for flexibility as well as for the correct orientation of commissural alignment (see Figure 3).
- A stiffer wire, such as the Double Curved Lunderquist™ Extra-Stiff Wire, should be used instead of other less stiff wires.
- A buddy peripheral balloon in the arch can redirect the THV delivery system enough to allow for crossing.
- Difficulty in crossing the aortic valve with the THV delivery system:
- This is encountered in cases with a horizontal aorta (aortoventricular angle > 60 degrees), especially with a dilated ascending aorta in computed tomography angiography (CTA), severe aortic valve calcification with bicuspid morphology, and in cases of a failed bioprosthetic aortic valve.
- In severely calcified aortic valves with a mean gradient above 50 mmHg, predilation with an undersized balloon should take place, particularly in cases of a Sievers type 0 and 1 bicuspid aortic valve or where there’s difficulty with delivering exchange catheters after wire crossing.
- For the SAPIEN 3 THV delivery system:
- Use the Edwards Commander delivery system to a different degree while advancing into the aortic valve.
- Put a stiff wire over the pigtail that can be placed in the aortic cusp or left ventricle to change the orientation of the aorta.
- While keeping “locked” in the inflation system, inflate 1 cc to the balloon in the THV delivery system to make a smoother transition between the crimped valve and the balloon — this accomplishes successful crossing most of the time.
- Perform a balloon aortic valvuloplasty (BAV) from the contralateral femoral access (a 12 mm balloon through a 6F sheath or a 20 mm balloon through a larger sheath), leaving the SAPIEN THV delivery system in the ascending aorta.
- Use the Chaperone Technique2 while pulling the snare placed at the tip or body of the Flex delivery system and advancing across the aortic valve closure (AOV).
- If the nose cone crosses the aortic valve but the crimped valve does not cross, the wire can be changed to a stiffer (or less stiff) wire for an alternative approach.
- For the Evolut PRO+ THV delivery system:
- Use the Double Curved LunderquistTM Extra-Stiff Wire in cases of a horizontal aorta with a high aorto-ventricular angle (> 60 degrees).
- Put the stiff wire over the pigtail catheter and place in the aortic cusp or left ventricle to change the orientation of the aorta.
- Perform a balloon aortic valvuloplasty (BAV) from the contralateral femoral
access (a 12 mm balloon through a 6 F sheath or a 20 mm balloon through the main larger sheath). - Use the Chaperone Technique2 to pull the snare and place it at the tip or body of the EnVeo PRO delivery system while advancing across the AOV (see Figure 4).
- For the Chaperone technique,2 we will lose wire access across the aortic valve, as we must place wire through the Goose Neck Snare before crossing the aortic valve. For the SAPIEN THV delivery system, we must prepare a new THV delivery system, as the former one can no longer be used at this point. Detailed steps include:
- Place the 25mm Goose Neck Snare in a 6 Fr catheter from the contralateral femoral or left radial access.
- Place the wire and the Amplatz Left (AL) catheter through the Goose Neck Snare in the descending aorta so that the stiff wire will be placed in the left ventricle across the aortic valve.
- Advance the THV delivery system over the stiff wire.
- Place the nose cone of the THV delivery system just above the aortic valve, then cinch down on the Goose Neck Snare to tighten at the nose cone or body of the THV delivery system after the crimp valve. While one operator pulls the THV delivery system toward a more favorable position for crossing, the other operator advances the more coaxial THV delivery system across the aortic valve.
- Loosen the Goose Neck Snare from the delivery catheter and bring it down to the descending aorta so as not to interact with THV deployment.
Summary
In this Tip-of-the-Month, different strategies for THV system delivery across the aortic valve in challenging cases are discussed. Of note, the more manipulations of the THV delivery system at the aortic arch and the ascending aorta we complete, the higher the risk of periprocedural stroke; thus, we should consider an alternative access in selected cases after analyzing TAVR CTA.
References
- Tang GHL, Zaid S, Fuchs A, et al. Alignment of Transcatheter Aortic-Valve Neo-Commissures (ALIGN TAVR): Impact on Final Valve Orientation and Coronary Artery Overlap. JACC Interv. 2020 May 11;13(9):1030–1042.
- Naganuma T, Kawamoto H, Hirokazu O, Nakamura S. Successful use of the loop snare technique for crossing a degenerated surgical valve with the Evolut-R system. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2019 Jun 1;93(7):E400–E402.
Figure 1: Flex Wheel in the Edwards Commander Delivery System
Figure 2: Flush Port in the EnVeo PRO Delivery System
Figure 3: Hat Marker of the THV Delivery System in the Outer Curvature
Figure 4: Chaperone Technique
Related QI Tips
Other evidence-based methods and tools you can use to improve quality of care and outcomes for patients.