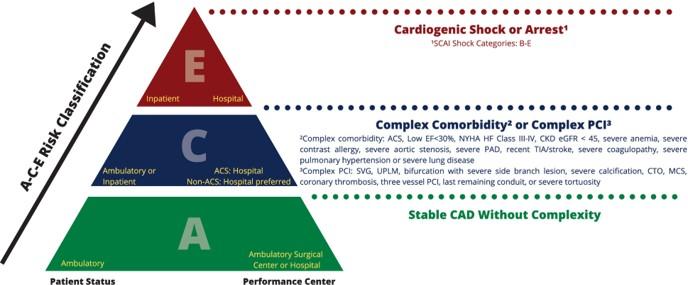
Americans with coronary artery disease
All authors: Robert F. Riley, MD, MS, FSCAI; Timothy D. Henry, MD, MSCAI; Ehtisham Mahmud, MD, MSCAI; Ajay J. Kirtane, MD, SM, FSCAI; Emmanouil S. Brilakis MD, PhD, FSCAI, Abhinav Goyal, MD; Cindy L. Grines, MD, MSCAI; William L. Lombardi, MD, FSCAI; Anbukarasi Maran, MD, FSCAI; Tanveer Rab, MD, FSCAI; Jennifer A. Tremmel, MD, MS, FSCAI; Alexander G. Truesdell, MD, FSCAI; Robert W. Yeh, MD, MSc, MBA, FSCAI; David X. Zhao, MD, FSCAI; and Farouc A. Jaffer, MD, PhD, FSCAI.
Other Guidance Documents
Evidence-based recommendations that promote optimal patient care based on current state-of-the-art science in interventional cardiology.
